SQL Joins
A JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
Different Types of SQL JOINs
Here are the different types of the JOINs in SQL:
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records when there is a match in either left or right table
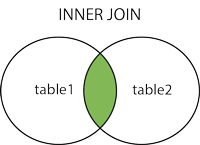
SQL INNER JOIN Keyword
The INNER JOIN keyword selects records that have matching values in both tables.
INNER JOIN Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Oracle INNER JOIN Example
Let's take an example to perform Inner Join on two tables "Suppliers" and "Order1".
Suppliers


Order1


This example will return all rows from "suppliers" and "order1" table where there is a matching supplier_id value in both the suppliers and order1 tables.
Execute the following query
- SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, suppliers.supplier_name, order1.order_number
- FROM suppliers
- INNER JOIN order1
- ON suppliers.supplier_id = order1.supplier_id;
Output

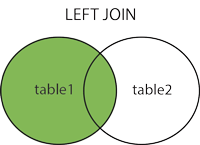
SQL LEFT JOIN Keyword
The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all records from the left table (table1), and the matched records from the right table (table2). The result is NULL from the right side, if there is no match.
Syntax
- SELECT columns
- FROM table1
- LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table2
- ON table1.column = table2.column;
Note: In some databases LEFT JOIN is called LEFT OUTER JOIN.
Execute this query
- SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, suppliers.supplier_name, order1.order_number
- FROM suppliers
- LEFT OUTER JOIN order1
- ON suppliers.supplier_id = order1.supplier_id;
Output

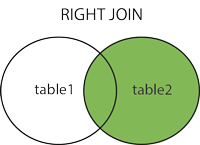
SQL RIGHT JOIN Keyword
The RIGHT JOIN keyword returns all records from the right table (table2), and the matched records from the left table (table1). The result is NULL from the left side, when there is no match.
RIGHT JOIN Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Note: In some databases RIGHT JOIN is called RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
Execute this query
- SELECT order1.order_number, order1.city, suppliers.supplier_name
- FROM suppliers
- RIGHT OUTER JOIN order1
- ON suppliers.supplier_id = order1.supplier_id;
Output

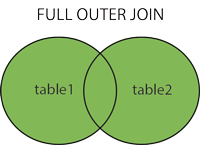
SQL FULL OUTER JOIN Keyword
The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword return all records when there is a match in either left (table1) or right (table2) table records. It places NULL where the join condition is not met.
Note: FULL OUTER JOIN can potentially return very large result-sets!
FULL OUTER JOIN Syntax
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
Below is a selection from the "Customers" table:
| CustomerID | CustomerName | ContactName | Address | City | PostalCode | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alfreds Futterkiste | Maria Anders | Obere Str. 57 | Berlin | 12209 | Germany |
| 2 | Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | Ana Trujillo | Avda. de la Constitución 2222 | México D.F. | 05021 | Mexico |
| 3 | Antonio Moreno Taquería | Antonio Moreno | Mataderos 2312 | México D.F. | 05023 | Mexico |
And a selection from the "Orders" table:
| OrderID | CustomerID | EmployeeID | OrderDate | ShipperID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10308 | 2 | 7 | 1996-09-18 | 3 |
| 10309 | 37 | 3 | 1996-09-19 | 1 |
| 10310 | 77 | 8 | 1996-09-20 | 2 |
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
FROM Customers
FULL OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
A selection from the result set may look like this:
| CustomerName | OrderID |
|---|---|
| Alfreds Futterkiste | |
| Ana Trujillo Emparedados y helados | 10308 |
| Antonio Moreno Taquería | 10365 |
| 10382 | |
| 10351 |
Note: The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword returns all the rows from the left table (Customers), and all the rows from the right table (Orders). If there are rows in "Customers" that do not have matches in "Orders", or if there are rows in "Orders" that do not have matches in "Customers", those rows will be listed as well.

Comments
Post a Comment