Object Pool Pattern
Object Pool Pattern
Object Pool Pattern says that " to reuse the object that are expensive to create".
Basically, an Object pool is a container which contains a specified amount of objects. When an object is taken from the pool, it is not available in the pool until it is put back. Objects in the pool have a lifecycle: creation, validation and destroy.
Advantage of Object Pool design pattern
- It boosts the performance of the application significantly.
- It is most effective in a situation where the rate of initializing a class instance is high.
- It manages the connections and provides a way to reuse and share them.
- It can also provide the limit for the maximum number of objects that can be created.
Usage:
- When an application requires objects which are expensive to create. Eg: there is a need of opening too many connections for the database then it takes too longer to create a new one and the database server will be overloaded.
- When there are several clients who need the same resource at different times.
NOTE: Object pool design pattern is essentially used in Web Container of the server for creating thread pools and data source pools to process the requests.
Example of Object Pool Pattern:
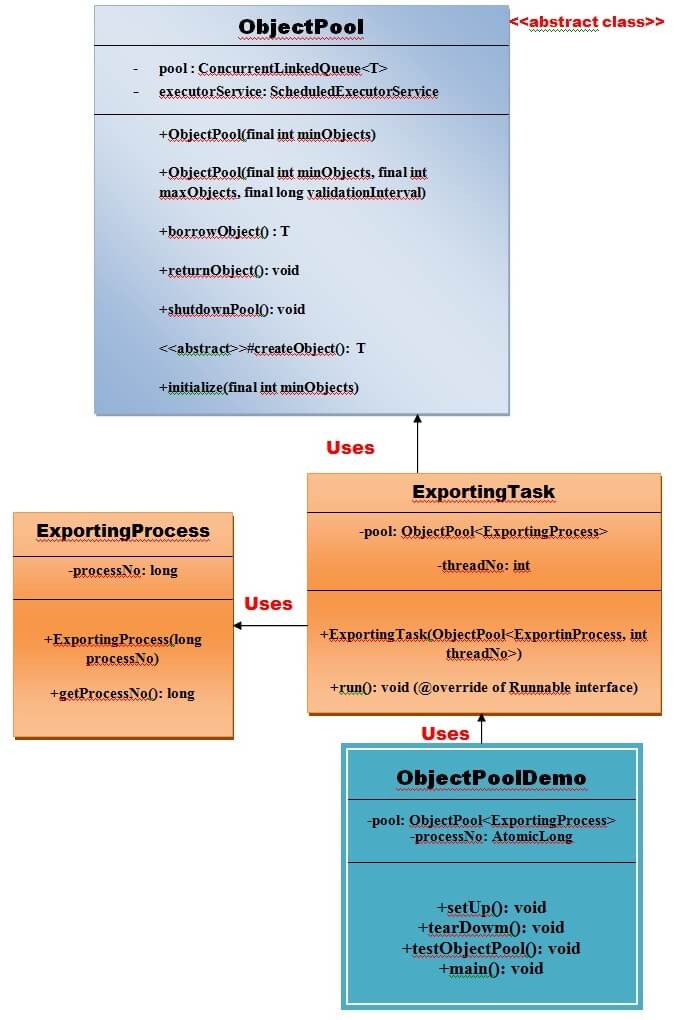
Let's understand the example by the given UML diagram.
UML for Object Pool Pattern
Implementation of above UML:
Step 1
Create an ObjectPool class that is used to create the number of objects.
File: ObjectPool.java
Step 2
Create an ExportingProcess class that will be used by ExportingTask class.
File: ExportingProcess.java
Step 3
Create an ExportingTask class that will use ExportingProcess and ObjectPool class.
File: ExportingTask.java
Step 4
Create an ObjectPoolDemo class.
File: ObjectPoolDemo.java
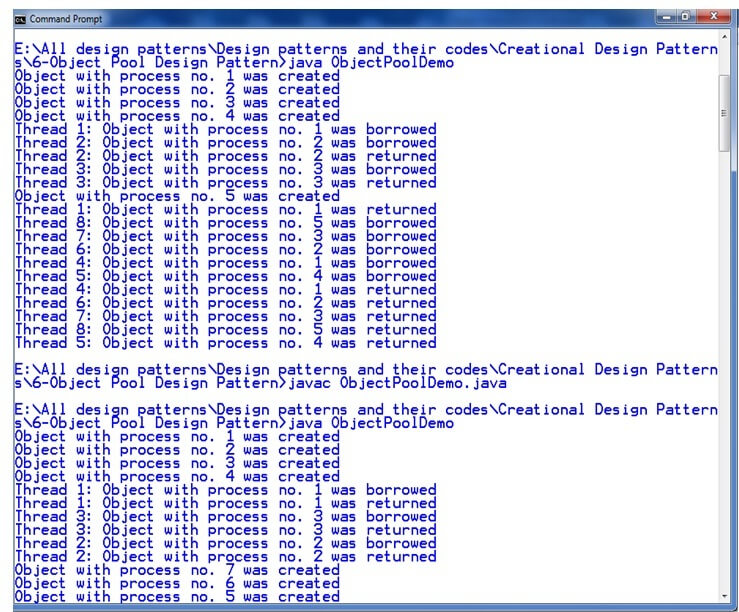
Output

Comments
Post a Comment