Template Pattern
Template Pattern
A Template Pattern says that "just define the skeleton of a function in an operation, deferring some steps to its subclasses".
Or, Template method design pattern is to define an algorithm as skeleton of operations and leave the details to be implemented by the child classes. The overall structure and sequence of the algorithm is preserved by the parent class.
Template means Preset format like HTML templates which has fixed preset format.Similarly in template method pattern,we have a preset structure method called template method which consists of steps.This steps can be abstract method which will be implemented by its subclasses.Benefits:
- It is very common technique for reusing the code.This is only the main benefit of it.
Usage:
- It is used when the common behavior among sub-classes should be moved to a single common class by avoiding the duplication.
UML for Template Pattern:

Implementation of Template Pattern:
Step 1:
Create a Game abstract class.
Step 2:
Create a Chess class that will extend Game abstract class for giving the definition to its method.
Step 3:
Create a Soccer class that will extend Game abstract class for giving the definition to its method.
Step 4:
Create a TemplatePatternDemo class.
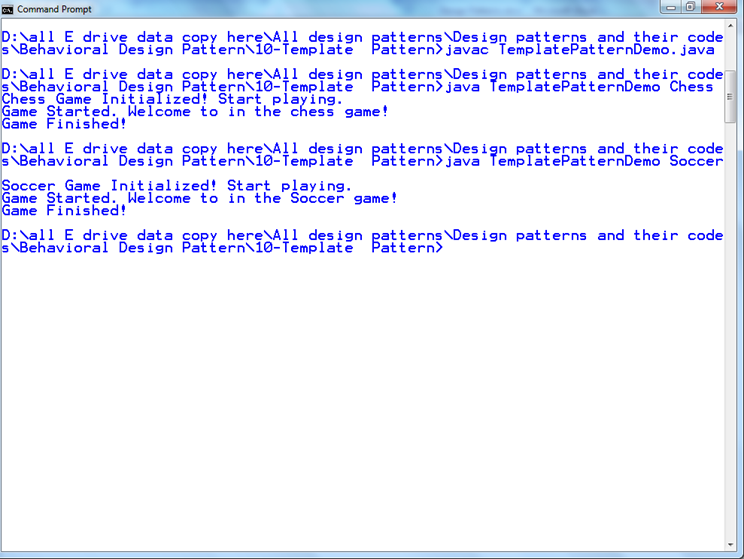
Output:

Comments
Post a Comment